No system is perfect, and in the dynamic world of industrial operations, challenges inevitably arise in the form of non-conformances, which can disrupt processes, compromise product integrity, and impact overall operational efficiency. But what if you could minimize these disruptions, turning potential setbacks or risks into opportunities for improvement? An efficient, well-equipped non-conformance management system paves the way for this to be possible.
Effectively managing non-conformances requires a proactive approach, robust strategies, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Businesses should constitute a non-conformance system involving these elements to address non-conformances and prevent recurrence swiftly.
Understanding Non-Conformances
Non-conformances refer to deviations from established standards, specifications, or requirements. In industrial operations, these deviations can manifest in diverse forms, ranging from product defects and process failures to regulatory violations and documentation errors. These deviations can result in rework, product recalls, and decreased productivity.
Non-conformance indicates a failure in a service, process, product, or system to meet specified requirements. It suggests that certain aspects of a company’s standard operating procedures are either not being followed or need modification.
Each type of non-conformance carries its own implications, necessitating tailored approaches for identification, assessment, and resolution. Non-conformances can be identified through internal and external audits, customer complaints, material inspections, or routine testing, leading to the preparation of a non-conformance report.
Challenges Posed by Non-Conformances
Non-conformances in industrial operations can lead to a range of significant consequences, impacting various aspects of the business. Comprehending these challenges is vital for implementing effective solutions and maintaining operational excellence.
I.Quality Issues
Non-conformances often result in defective products or services that fail to meet customer expectations. This can lead to:
- Customer Dissatisfaction: Inferior products can cause dissatisfaction among customers, leading to complaints, returns, and loss of repeat business.
- Increased Inspection and Testing: Additional resources must be allocated for quality checks and testing to identify and rectify defects, driving up operational costs.
- Waste and Scrap: Higher levels of waste and scrap material due to non-conforming products can significantly impact the bottom line and sustainability efforts.
II. Compliance Risks
Violations of regulatory requirements due to non-conformances can have severe repercussions:
- Fines and Penalties: Companies may face substantial fines and penalties for failing to comply with industry standards and regulations.
- Legal Consequences: Non-compliance can lead to legal actions, resulting in costly litigation and settlements.
- Loss of Certifications: Regulatory bodies may revoke essential certifications, affecting the company’s ability to operate in certain markets and diminishing competitive advantage.
III. Operational Disruptions
Non-conformances can disrupt smooth operations, leading to:
- Production Delays: Errors and defects necessitate rework and corrective actions, causing delays in production schedules and delivery timelines.
- Increased Operational Costs: The need for rework, additional inspections, and corrective measures leads to higher operational expenses.
- Resource Allocation: Substantial time and resources must be diverted to address non-conformances, impacting overall productivity and efficiency.
IV. Reputation Damage
The long-term impact of non-conformances on brand reputation and customer trust can be profound:
- Negative Public Perception: Quality failures and compliance issues can attract negative publicity, tarnishing the brand’s image in the market.
- Customer Trust Erosion: Repeated non-conformances can erode customer trust, making it challenging to retain existing customers and attract new ones.
- Competitive Disadvantage: A damaged reputation can give competitors an edge, leading to a loss of market share and business opportunities.
In conclusion, non-conformances pose a multifaceted threat to industrial operations, affecting quality, compliance, performance, and reputation.
Levels of Non-Conformance
Non-conformances are often categorized into levels based on their severity and impact on quality, safety, or regulatory compliance. Common levels include:
⇒ Critical Non-Conformance
- Issues that pose significant risks to product safety, functionality, or compliance.
- Immediate corrective action is usually required to prevent severe consequences.
⇒ Major Non-Conformance
- Significant deviations from requirements that affect product quality or compliance.
- Corrective action is necessary to prevent recurrence and ensure customer satisfaction.
⇒ Minor Non-Conformance
- Minor deviations that do not significantly impact product quality or compliance.
- Correction is needed to maintain consistency and prevent potential escalation.
⇒ Observation or Opportunity for Improvement
- Areas for enhancement identified during audits or inspections.
- Actions are recommended to improve processes, efficiency, or compliance over time.
Types of Non-Conformance
Non-conformances can be categorized as given below:
- Product Non-Conformance: Product non-conformances involve deviations from product specifications or quality standards. These can include defects in manufacturing, variations in dimensions or materials, and functional failures that affect product performance or safety.
- Process Non-Conformance: Process non-conformances arise from failures to adhere to prescribed procedures or methods during manufacturing or operational processes. This may include deviations in workflow, improper equipment operation, or material handling issues that impact quality and efficiency.
- Documentation Non-Conformance: Documentation non-conformances involve errors or deficiencies in recording essential information, such as incomplete records, inaccurate data entry, or failure to maintain required documentation standards. These can hinder traceability, audits, and compliance assessments.
- Supplier Non-Conformance: Supplier non-conformances occur when suppliers fail to meet agreed-upon specifications, quality standards, or delivery schedules. Issues with suppliers can disrupt supply chain operations, affecting production timelines and product quality.
- Regulatory Non-Conformance: Regulatory non-conformances occur when operations or products fail to comply with applicable laws, regulations, or industry standards. These violations can lead to legal repercussions, fines, or loss of certifications, necessitating immediate corrective actions.
Strategies for Effective Management of Non-Conformances
Detecting non-conformance in the workplace requires a structured process that includes observing, documenting, analyzing, and implementing corrective measures. Non-conformance may stem from multiple factors, such as human errors, equipment failures, insufficient training, and procedural oversights. Here’s a fundamental guide to adequately handle non-conformances in an organization:
#1 Establish Clear Standards and Procedures
Define and communicate clear quality standards, procedures, and expectations across all levels of the organization. Ensure that employees understand their roles and responsibilities in adhering to these standards.
#2 Implement Quality Control Systems
Integrate quality control mechanisms throughout the production process to detect and address non-conformances in real time. Utilize technologies such as sensors, automated inspection systems, and data analytics to enhance quality monitoring and decision-making.
#3 Conduct Regular Audits and Inspections
Perform regular audits and inspections to assess compliance with quality standards, identify potential non-conformances, and evaluate the effectiveness of corrective actions. Document findings and communicate outcomes to relevant stakeholders for transparency and accountability.
#4 Promote a Culture of Quality and Accountability
Foster a culture where quality is prioritized at every stage of operations. Encourage open communication, collaboration, and feedback among teams to address issues promptly and diligently.
#5 Implement Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA)
Develop structured CAPA processes to systematically address non-conformances when they occur. Identify root causes, implement corrective actions to resolve immediate issues, and establish preventive measures to prevent recurrence.
#6 Provide Continuous Training and Development
Invest in ongoing training programs to enhance employee skills, knowledge, and awareness of quality standards and operational procedures. Empower employees to contribute to quality improvement initiatives through education and skill development.
#7 Utilize Data-Driven Decision Making
Leverage data analytics and performance metrics to monitor key quality indicators, identify trends, and make informed decisions regarding process improvements and risk mitigation strategies.
#8 Collaborate with Suppliers and Stakeholders
Establish collaborative relationships with suppliers and stakeholders to ensure alignment on quality expectations, specifications, and continuous improvement initiatives. Implement supplier quality management programs to monitor and manage supplier performance effectively.
Role of CAPA Software Solutions in Non-Conformance Management
Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) software solutions play a central role in managing non-conformances successfully as they are specialized tools to streamline the entire CAPA process, from identification and investigation to resolution and prevention. Key functionalities of CAPA software include:
Incident Reporting: A centralized platform for employees to report non-conformances and incidents promptly.
Root Cause Analysis: Tools for conducting thorough investigations to determine the underlying causes of non-conformances.
Action Planning: Automated workflows for defining and assigning corrective and preventive actions to responsible teams or individuals.
Tracking and Monitoring: Real-time dashboards and analytics to monitor CAPA progress and ensure timely completion of actions.
Documentation and Audit Trails: Comprehensive documentation of CAPA activities to demonstrate compliance during audits and inspections.
By leveraging CAPA software solutions, organizations can organize non-conformance management, augment operational efficiency, and mitigate risks associated with quality issues and compliance breaches. Embracing a culture of constant improvement and risk management will not only protect business reputation and customer trust but also drive sustainable growth and competitiveness in the dynamic industrial landscape. In conclusion, investing in CAPA software solutions is not just a strategic choice but a necessity for organizations committed to achieving mastery in non-conformance management and ensuring long-term success in industrial operations.
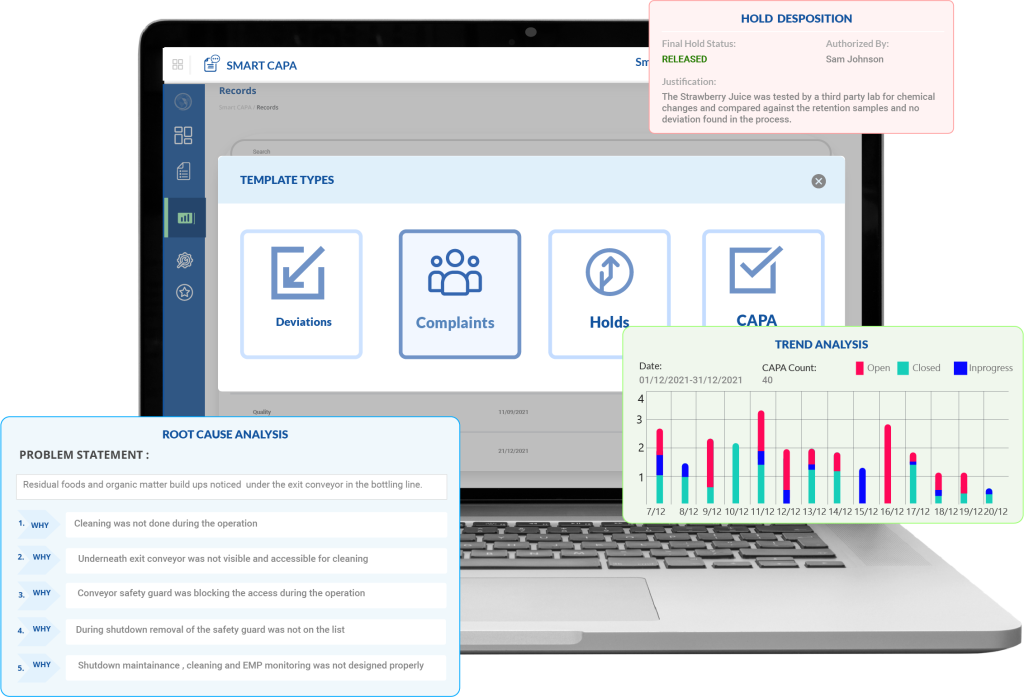
Smart CAPA: One-Stop Digital Solution for Non-Conformance Management
Most non-conformance procedures are reactive and defensive, leaving quality managers frustrated as they struggle within a system that seems to work against proactive, preventive measures. Smart CAPA offers a transformative digital solution designed to break this cycle.
Smart CAPA is an efficient corrective and preventive action management software solution that streamlines and automates the management of complaints, holds, and deviations within an organization. It provides an orderly system for identifying, investigating, and resolving issues or non-conformities, while also proactively implementing measures to prevent their recurrence.
Our platform equips enterprises with advanced tools for real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated compliance checks, enabling a shift from reactive to proactive non-conformance management. By integrating smooth workflows and robust reporting features, Smart CAPA empowers quality managers to rectify potential non-conformances before they escalate, ensuring continuous improvement and bringing an environment of high standards to any business.